|
See also
UCLUST algorithm
Abundance sort
Sort order
UCLUST assumes that input sequences are sorted in an order such that an
appropriate centroid sequence is found before other members of its cluster. The two most common sort orders
are
summarized in the table below.
|
Order |
Description |
|
Decreasing length |
This order is most appropriate when input sequences
have large variations in length, e.g. because full-length sequences and
fragments are both present, as shown in the figure below. However, with a length sort, the longest sequence may be an
outlier. This can be addressed by recentering.
|
|
Decreasing abundance |
See abundance sorting.
|
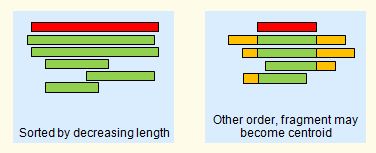
Multiple alignment of a cluster.
The centroid (representative) sequence is shown in red.
Fragments are poor centroids because member sequences may be
dissimilar in the regions that do not align to the fragment (orange).
|